Last updated on March 29th, 2022 , 09:51 am
Volatility has become a tradable asset class due to the success of volatility ETPs such as VXX, SVXY, and UVXY.
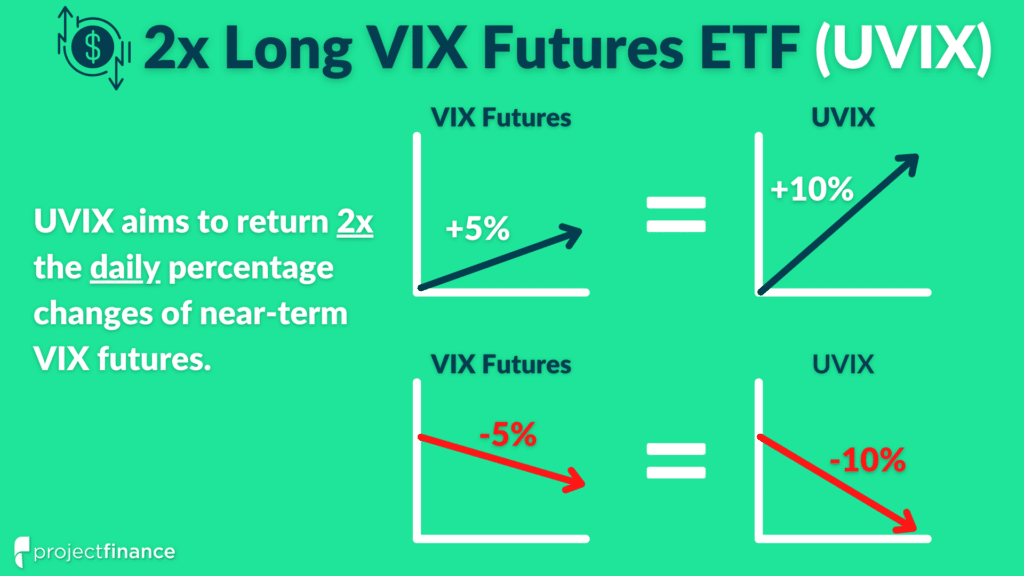
UVIX is one of the newest products entering the volatility trading space, restoring the 2x leveraged long volatility exposure that UVXY once had.
Jump To
What is UVIX and How Does it Work?
UVIX gains value as VIX futures rise and loses value as VIX futures fall.
Bullish allocations to UVIX are long volatility, while bearish allocations to UVIX are short volatility.Trading UVIX
The inception date of UVIX is scheduled to be March 30th, 2022. Volatility Shares is the issuer of UVIX.
Let’s explore the Long VIX Futures Index mentioned in the product description to learn how UVIX works.
What is the Long VIX Futures Index (LONGVOL)?
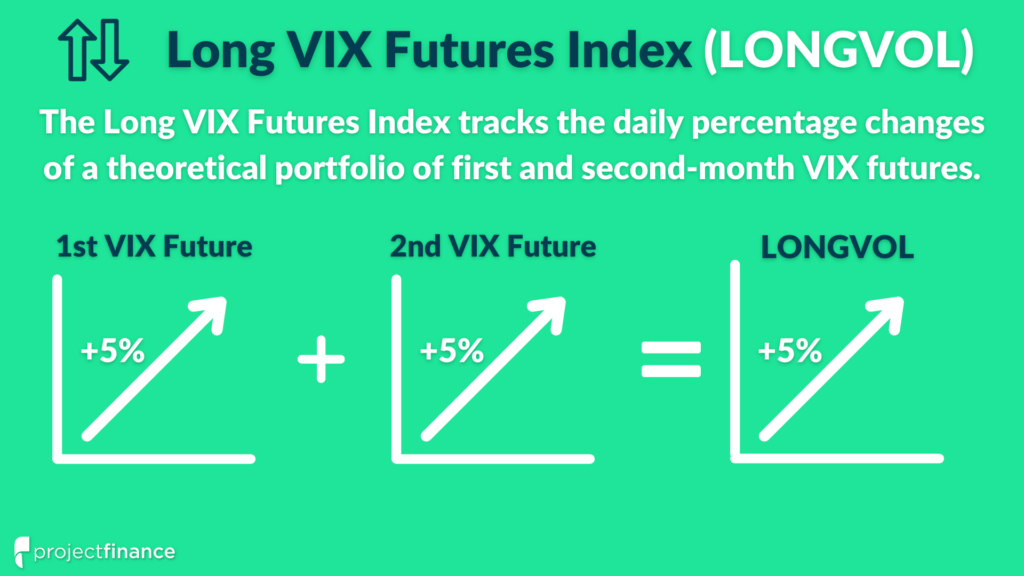
The benchmark UVIX tracks is the Long VIX Futures Index (LONGVOL) by Cboe.
Index Methodology: LONGVOL tracks the daily performance of a theoretical portfolio of first and second-month VIX futures contracts that are rolled daily. The portfolio aims to hold a mixture of the two futures to achieve a weighted average of 30 days to settlement.
If it is February 1st, the first-month VIX future will be the February contract, and the second-month VIX future will be the March contract.
VIX futures track the Cboe Volatility Index (the VIX Index), which increases during times of heightened market volatility and falls during calm market periods.
A long VIX futures position profits when the:
VIX index increases to higher levels, pulling VIX futures contracts up along with it.
VIX futures curve is in backwardation, causing short-term futures to drift higher as they converge towards the higher VIX index.
The LONGVOL index will therefore increase during rising or persistently high volatility market conditions where VIX futures are in backwardation.
Bullish UVIX traders are effectively long Cboe volatility index futures.
Bearish UVIX traders are effectively short Cboe volatility index futures.
LONGVOL Movement Examples
The past performance of the LONGVOL index informs us about how UVIX should perform under various market conditions:
During extended periods of low volatility, UVIX will lose substantial value driven by consistent contango in the VIX futures market, leading to decaying near-term VIX Futures.
VIX Contango: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
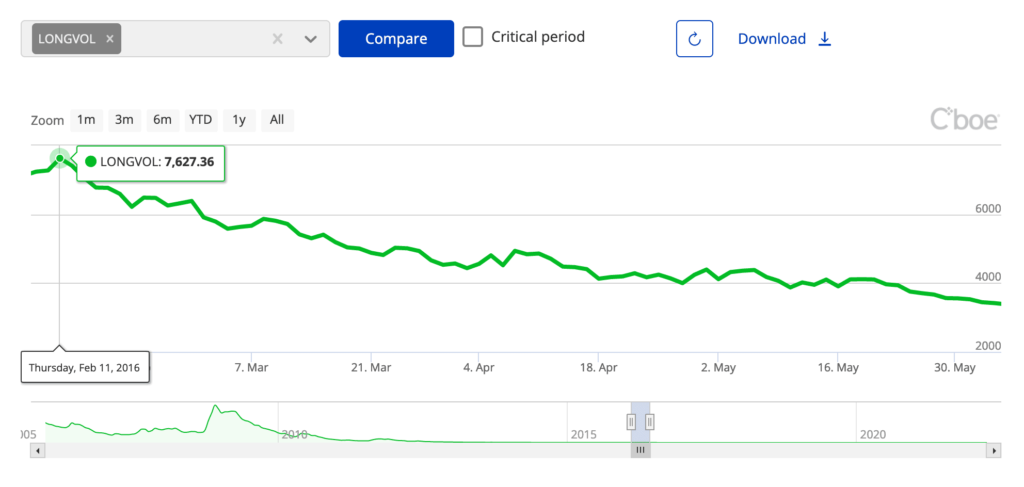
Consequently, the share price of UVIX will decay immensely, as LONGVOL did during the persistently low volatility of 2016. Here is LONGVOL during the first few months of 2016:
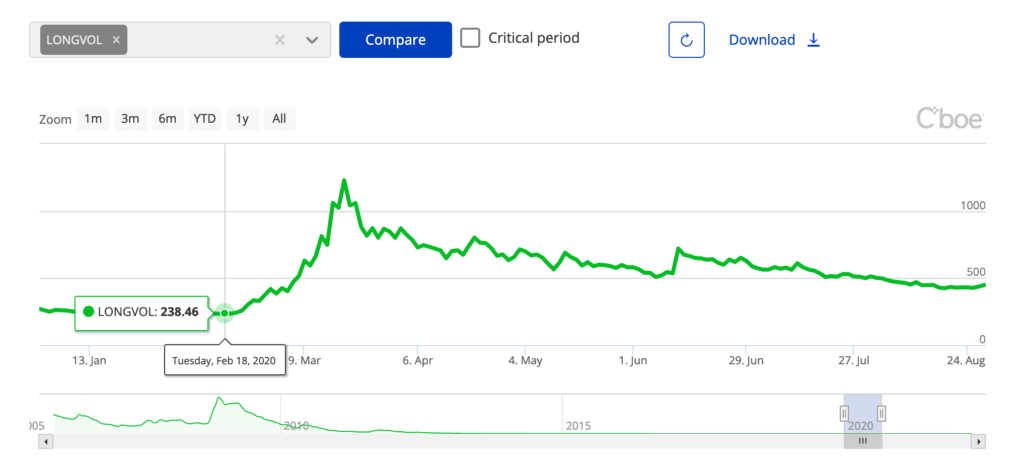
From February 2016 to June 2016, LONGVOL fell from 7,600 to around 3,600, a decrease of over 50%. UVIX would have experienced an even worse decline, as it tracks 2x the daily percentage change of LONGVOL.
But during periods of surging market volatility, UVIX will gain significant value. The faster the increase in volatility, the larger the increase UVIX will experience.
Here’s what LONGVOL did in early 2020:
Source: Cboe
If you’re familiar with UVXY, it used to have 2x long volatility exposure like UVIX. After the “volmageddon” of 2018, UVXY’s leverage was reduced from 2x to 1.5x.
UVIX is the new 2x long volatility product, restoring the previously accessible 2x leverage to the long volatility product space.
While UVIX may experience exponential returns during periods of rapidly increasing or persistently high volatility, the long-term trend in UVIX will be down as VIX futures are in contango a majority of the time during normal market conditions.

New to options trading? Learn the essential concepts of options trading with our FREE 160+ page Options Trading for Beginners PDF.
What is the Difference Between VIX and UVIX?
The VIX cannot be traded directly. UVIX allows positive leveraged exposure to changes in the VIX index through the VIX futures market.
The Cboe VIX Index is a calculation of market implied volatility using S&P 500 Index options with around 30 days to expiration.
The VIX index cannot be traded as there are no underlying shares. It is only a calculation.
To trade anticipated changes in the VIX index, traders turn to VIX futures and options.
Trading VIX futures is a risky endeavor, as one VIX futures contract represents $1,000 per point in notional value (a large position). A 10-point move in a VIX futures position translates to a P/L of $10,000 on one contract.
UVIX is an ETF that tracks the LONGVOL index, which tracks 2x the single-day percentage changes of the first and second-month VIX futures contracts.
For instance, if it is February 1st, LONGVOL will track 2x the single-day percentage changes of a mixed portfolio of February and March VIX futures contracts.
UVIX is a volatility product that allows traders to gain leveraged exposure to changes in the VIX index through the futures market.
VIX Index <= VIX Futures <= UVIX
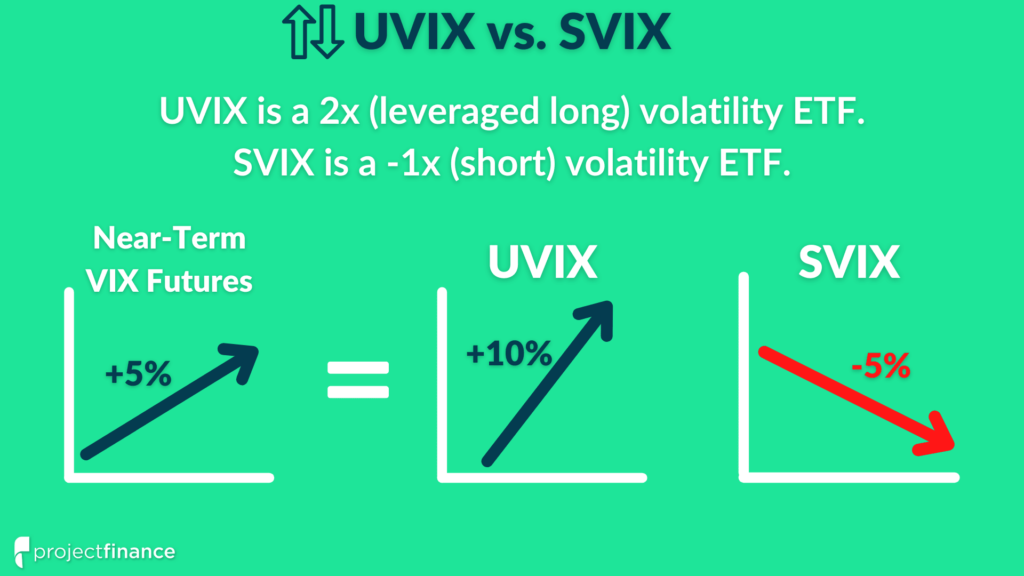
What is the Difference Between UVIX and SVIX?
UVIX, the 2x Long VIX Futures ETF, seeks to provide daily investment returns, before fees and expenses, that correspond to twice the performance of the Long VIX Futures Index (LONGVOL).
UVIX is a 2x leveraged long volatility product.
UVIX aims to return 2x the daily percentage change of a portfolio consisting of first and second-month VIX futures contracts.
SVIX, the Short VIX Futures ETF, seeks to provide daily investment returns, before fees and expenses, that correspond to the performance of the Short VIX Futures Index (SHORTVOL).
SVIX is a short volatility product.
SVIX aims to return -1x the daily percentage change of a portfolio consisting of first and second-month VIX futures contracts.
How Risky is UVIX?
UVIX is a high-risk leveraged volatility product.
UVIX should not be held as a long-term “investment.” Buying shares of UVIX does not represent ownership of any business, unlike buying shares of SPY.
During calm market periods where the VIX futures are in contango, UVIX will lose value steadily from the decaying VIX futures.
The investment strategy of holding UVIX during low market volatility with the anticipation of increasing market volatility is not easy.
In the event of a short-term volatility spike, UVIX can gain significant value, but over time, it should trend towards zero.
UVIX is designed for short-term stock and options trading, not long-term “investing.” It is incredibly expensive to hold long volatility positions constantly, as VIX futures lose value when in prolonged periods of contango.
Additionally, the complex nature of UVIX can cause uninformed traders to lose money due to a lack of understanding of the product’s mechanics.
I do not recommend making any trades in UVIX unless confident in your understanding of how it works, and the risks of your specific trades.
How is UVIX Calculated?
UVIX is benchmarked to the Long VIX Futures Index (LONGVOL).
LONGVOL tracks the daily performance of a theoretical portfolio of first and second-month VIX futures contracts that are rolled daily.
Each day, the net asset value (NAV) of UVIX should correspond to:
Previous Closing Price + 2x the Current Trading Day’s LONGVOL Change (%)
Example: UVIX closes at $50 on Monday.
On Tuesday, if the LONGVOL index increases by 3%, UVIX shares should trade 6% higher at $53 ($50 x 1.06).
Conversely, if the LONGVOL index falls by 10%, UVIX shares should fall 20% to $40 ($50 x 0.80).
The above examples represent no tracking error (perfect tracking of index performance). In reality, exchange-traded products can experience tracking error.
Source: UVIX Prospectus (p.36)
Is There Options Trading on UVIX?
UVIX is a brand new product (inception date of March 30th, 2022) and does not yet have a liquid options market. Time will tell if the options market in UVIX improves.
Does UVIX Pay a Dividend?
No, UVIX does not pay a dividend.
Additional Resources

About the Author
Chris Butler received his Bachelor’s degree in Finance from DePaul University and has nine years of experience in the financial markets.
Chris started the projectfinance YouTube channel in 2016, which has accumulated over 25 million views from investors globally.